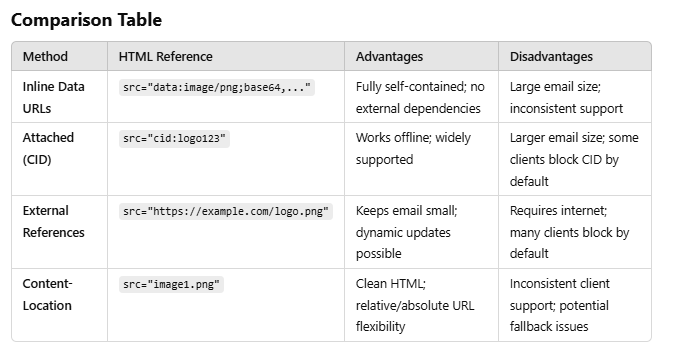
When including images in an HTML email , there are multiple ways to reference and embed the images.
*** Use Chilkat.Email.AddRelatedFile or ChilkatEmail.AddRelatedBd to add an image referenced using Content-ID
*** Use Chilkat.Email.AddRelatedFile2 or ChilkatEmail.AddRelatedBd2 to add an image referenced using Content-Location
1. Inline Data URLs
- Description: The image is embedded directly in the HTML as a Base64-encoded data URL within the “src” attribute of the “<img />” tag.
- How It Works:
- The image data is encoded in Base64 and included inline.
- No separate MIME part is needed for the image.
- Example:
<img src="data:;base64,iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAAAUA..." />
2. Attached Images Referenced by “Content-ID” (CID)
Supported by most email clients.
- Description: Images are included as separate MIME parts with a “Content-ID” header and referenced using the “cid:” scheme in the HTML.
- How It Works:
- Each image is attached as a MIME part with a unique “Content-ID”.
- The HTML references the image using “src=”cid:unique-id”.
- MIME Example:
Content-Type: multipart/related; boundary="boundary" --boundary Content-Type: text/html; charset="UTF-8" <html> <body> <img src="cid:logo123"> </body> </html> --boundary Content-Type: image/png Content-ID: <logo123> iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAAAUA... --boundary--
3. External Image References
Not recommended because most email clients block external images by default for privacy and security reasons.
- Description: The HTML references images hosted on an external server using an absolute URL in the “src” attribute.
- How It Works:
- The email client fetches the image from the specified URL at the time of display.
- Example:
<img src="https://example.com/images/logo.png" />
4. Attached Images Referenced by “Content-Location”
Inconsistent support across email clients (less supported than “Content-ID”).
- Description: Images are included as separate MIME parts with a “Content-Location” header, which provides a relative or absolute URL that the HTML can reference.
- How It Works:
- The “Content-Location” header associates a MIME part with a name or URL.
- The HTML references the image using the same value in the “src” attribute.
- MIME Example:
Content-Type: multipart/related; boundary="boundary" --boundary Content-Type: text/html; charset="UTF-8" <html> <body> <img src="image1.png"> </body> </html> --boundary Content-Type: image/png Content-Transfer-Encoding: base64 Content-Location: image1.png iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAAAUA... --boundary--